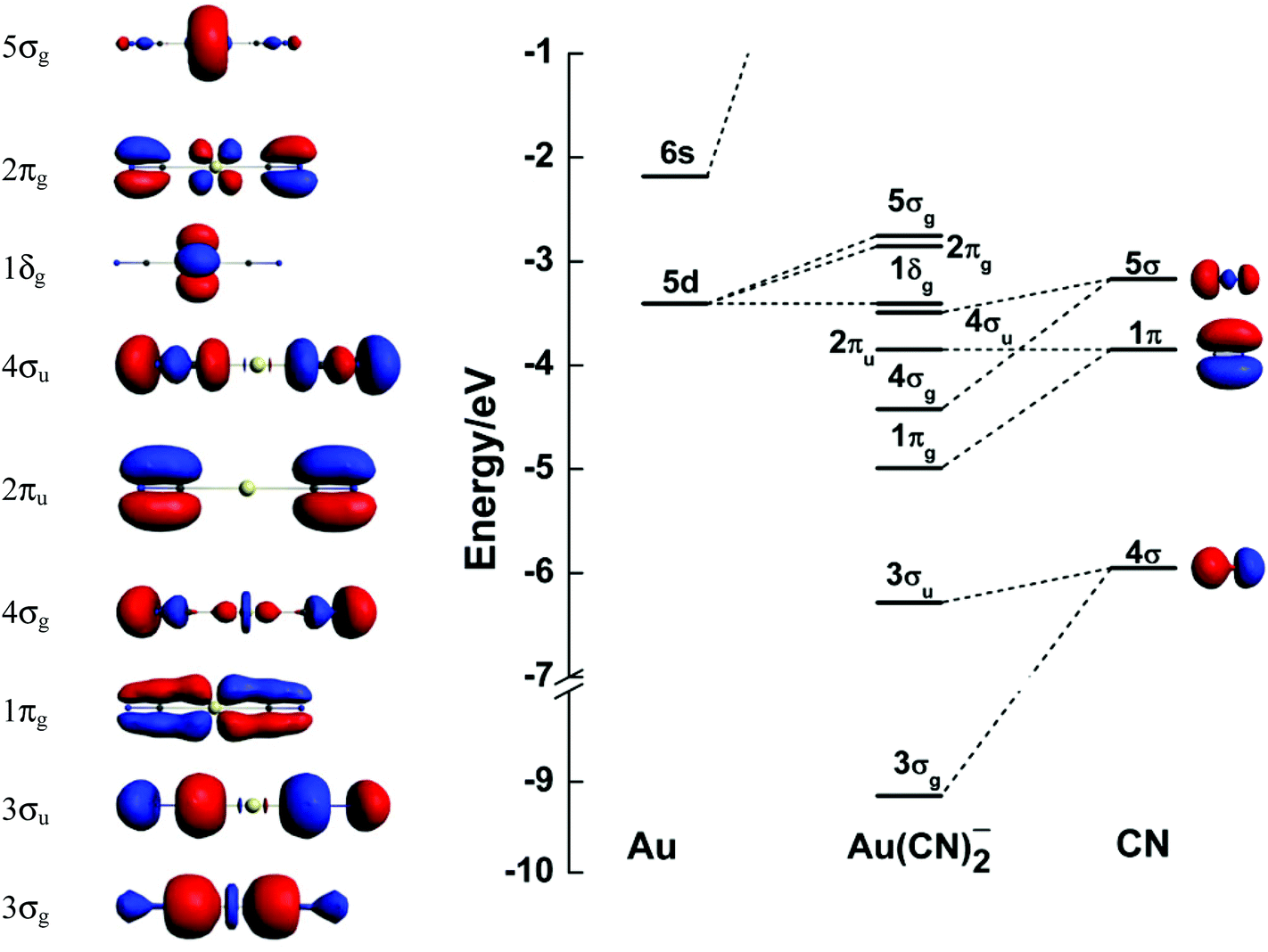
S D Orbital Overlap

Both d xz and d yz can form π bonds with each other.
S d orbital overlap. In picture 1 we show the molecular orbital structure of f2. D z 2 is capable of forming a σ interaction with another d z 2. These diagrams show the origin of σ π and δ bonding between two d orbitals aligned along the z axis. Positive overlapping of atomic orbital when the phase of two interacting orbitals is same then.
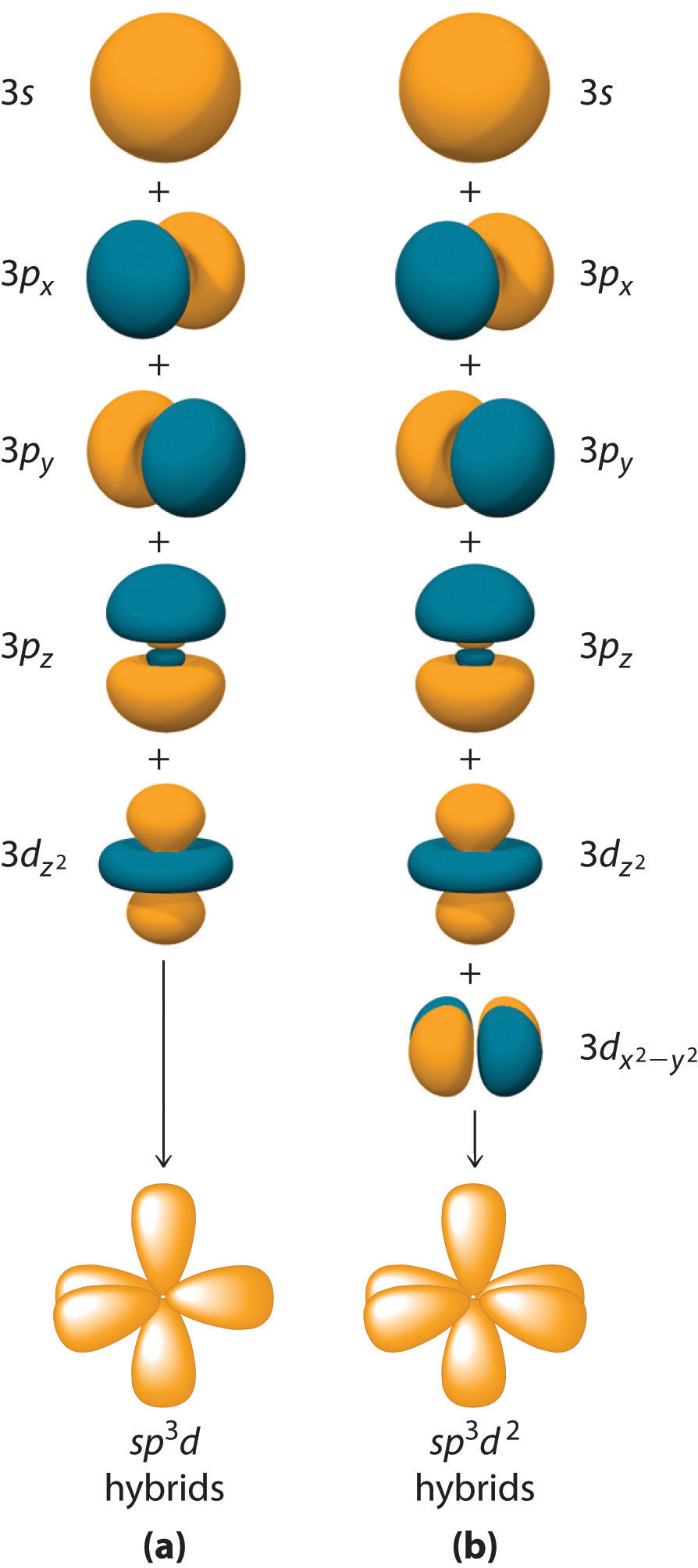
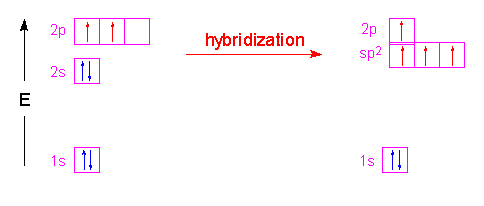
There are totally 5 d orbitals which are named as d z 2 d xy d xz d yz and d x 2 y 2. D x 2 y 2 and d xy can interact with each other to form δ bonds. Learn more about atomic orbital at byjus. The importance of orbital overlap was emphasized by linus pauling to explain the molecular bond angles observed through experimentation and is the basis for the concept of orbital hybridization.
Orbitals chemistry s p d and f orbital atomic orbitals are of four different kinds denoted s p d and f each with a different shape. Of the four we ll be concerned primarily with s and p orbitals because these are the most common in organic chemistry. This overlap may involve s s s p s d or even p d orbitals. Mo from d orbitals.
This makes the π bond a weaker bond than the original σ bond that connects two neighboring atoms. Formation of a hydrogen molecule from two hydrogen atoms. Start from the third row all the elements after sodium na have d orbitals. S s orbital overlap formation of h 2 molecule.
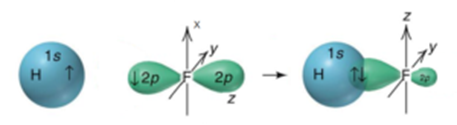
In the case of s and p orbitals there can be three types of overlap. The h1s orbital overlap with one of the f2p orbitals. P orbital overlap is less than head on overlap between two s orbitals in a σ bond due to orbital orientation. This simply means that electron density is highest along the axis of the bond.
σ z y x σ x y z construct the molecular orbital diagram for. In picture 2 we show the overlapping p orbitals which form the bond between the two fl uorine atoms in red and green gradients. The mutual overlap between the half filled s orbitals of two atoms is called s s overlap and the covalent bond formed is known as sigma s bond. Since s orbitals are spherical and have no directionality and p orbitals are oriented 90 to each other a theory was needed to explain why molecules such as methane ch 4 had observed bond angles.
Atoms combine together to lower down the energy of the system to attain stability in layman s terms the rule simply says that the less energy you need the easier for you to survive for example hydrogen prefers to exist as h 2 molecule instead of isolated hydrogen atom because h 2 requires lesser energy than isolated h atom. Overlapping of atomic orbital. However the fact that its strength is added to the underlying σ bond bond makes for a stronger overall linkage. The dashed lines show the remaining p orbitals which do not take part in the bonding.
Overlapping of atomic orbitals. Single covalent bonds that form between nuclei are created from the head to head overlap of orbitals and are called sigma s bonds.